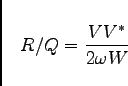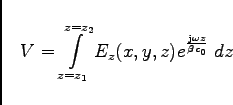Next: R/Q: Real fields
Up: Supplied Macros
Previous: Q-Values: Complex fields
Contents
There are several definitions for a normalized shunt impedance floating around.
We take this one:
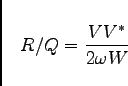 |
(4.2) |
where
 is the normalized shunt impedance,
is the normalized shunt impedance,
 is the complex voltage that would be seen by a test charge traversing
the cavity at a speed of
is the complex voltage that would be seen by a test charge traversing
the cavity at a speed of  ,
,
 is the circular frequency of the mode,
is the circular frequency of the mode,
 is the total stored energy in the cavity
(both electric and magnetic energy).
is the total stored energy in the cavity
(both electric and magnetic energy).
If one evaluates the voltage seen by the test particle, one arrives at
the result
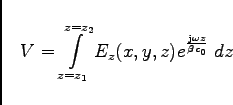 |
(4.3) |
for a particle that travels in positive z-direction from  to
to  .
.
Subsections