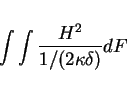 |
-losses.
Its menu is:
############################################################################## # Flags: nomenu, prompt, message, # ############################################################################## # section: -losses # ############################################################################## # symbol = e_1 # # quantity = e # # solution = 1 # # # # # # @metalpower : undefined (symbol: undefined) # ############################################################################## # doit, ?, return, end, help # ##############################################################################Since the power losses are caused by currents flowing in metal, and the currents are proportional to the tangential H-field at the metallic walls, we have to enter a H-field as
smybol or quantity.
-losses
quantity= h
solution= 1
doit
The wall losses are computed as:
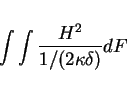 |
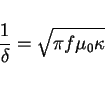 |
The integral is performed over all metallic surfaces that would appear in a plot as produced by the section -3darrowplot. This implies, that wall losses are NOT computed for electric symmetry planes, since the material on the symmetry planes are not shown in -3darrowplot.
The conductivities that are used in the pertubation formula may be entered in the section -material. The result of the computation is available as the symbolic variable @metalpower.
The resulting menu (with the default conductivities of copper) is
############################################################################## # Flags: nomenu, prompt, message, # ############################################################################## # section: -losses # ############################################################################## # symbol = h_1 # # quantity = h # # solution = 1 # # # # # # @metalpower : 16.49728e-06 (symbol: h_1) # ############################################################################## # doit, ?, return, end, help # ##############################################################################